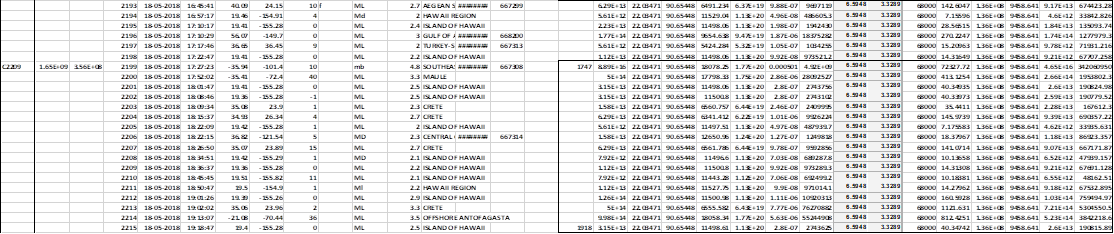
Note: The above is the excel file for Table 2 in the article below. Table 2 may not be legible enough.
By Ramaswami Ashok Kumar B.E., M.E., Negentropist, Bombay Sarvodaya Mandal, 299, Tardeo Road, Nana Chowk, Mumbai-400007
© 2022-2023 Ramaswami Ashok Kumar
Invocation
https://m.youtube.com/watch?v=x_TIBv6Z4es&list=RDMM31vQFHBhJoQ&index=14
The method of analysis.
380 flights covered in (1) are examined for normal and abnormal flights.
These flights are subdivided into sets as in Table 1. Each set contains normal and abnormal flights in a time series. Earthquakes(all caused by dams) are used as proxy to determine the world dam content changes. At the location of the airplane, the acceleration of the airplane is determined due to the sudden application of force by the dam content change(Force applied by the dams from their centre of gravity/mass of the airplane at take off). Further the distance from the airplane to the centre of gravity is determined to compute the bending moment that is suddenly applied to the plane by the world’s dams(Force x distance) in Newton-meters or Joules. The energy required to raise the temperature of the airplane by 1 degree Kelvin is then determined knowing the specific energy of the plane(assumed as 2000J/kg/K). Thus from this data the sudden temperature rise of the plane is estimated as the world dam dynamic water moment hits the plane for a millisecond or five. To get a ballpark estimate of the temperature rise, Lagos is chosen as the location of the airplane in flight for all the sets. Since the location of the plane within Nigeria is around (Lat 9, Long 9) we can always rework to get at the accurate result. But the final result is not altered by the simplification introduced(Table 2).
The correlation of number of abnormal flights with the world dam dynamics applied shock input temperatures,K, Nigeria 18May 2018 to 3 January 2019 is shown in Fig 1Ch3: 96% of the variations of the abnormal flights are explained by the square of the 6th degree polynomial correlation, R^2= 0.959, with World Dam Dynamics induced shock input temperatures.